A lipoma is a benign (non-cancerous) growth of fatty tissue that typically appears just below the skin. They are usually soft to the touch, moveable, and painless. Lipomas can appear anywhere on the body but are most commonly found on the neck, shoulders, back, abdomen, arms, or thighs.
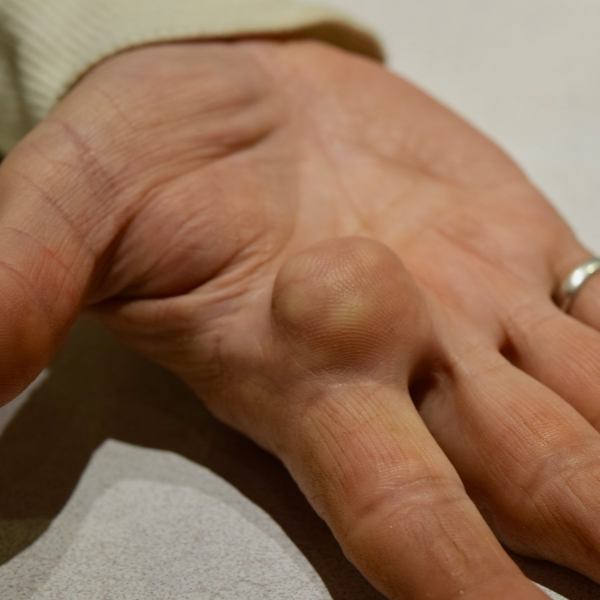
A lipoma is a benign (non-cancerous) growth of fatty tissue that typically appears just below the skin. They are usually soft to the touch, moveable, and painless. Lipomas can appear anywhere on the body but are most commonly found on the neck, shoulders, back, abdomen, arms, or thighs.
The exact cause of lipomas is unknown, but they tend to run in families and are more common in people who are overweight. They can also be caused by trauma to the area.
Anyone can develop a lipoma, but they are more common in middle-aged adults and people who are overweight.
Lipomas typically do not require treatment unless they are causing discomfort, are in a visible location, or are growing rapidly. If a lipoma needs to be removed, it can usually be done under local anesthesia in a dermatologist’s office or outpatient surgery center. The surgeon will make a small incision in the skin, remove the lipoma, and then close the incision with sutures or sterile-strips.
The area around the lipoma will be numbed with local anesthesia, so you should not feel any pain during the procedure. You may feel some pressure or tugging sensations, but these should not be painful.
Lipoma removal is usually a quick procedure that can be done in less than an hour. However, the exact time will depend on the size and location of the lipoma.
After the procedure, you will be given instructions on how to care for the incision site and when to remove any dressings or bandages. You may experience some swelling, bruising, and discomfort in the area for a few days, but this should subside within a week or two. You should avoid strenuous activity and heavy lifting for at least a week after the procedure to allow the incision to heal properly.